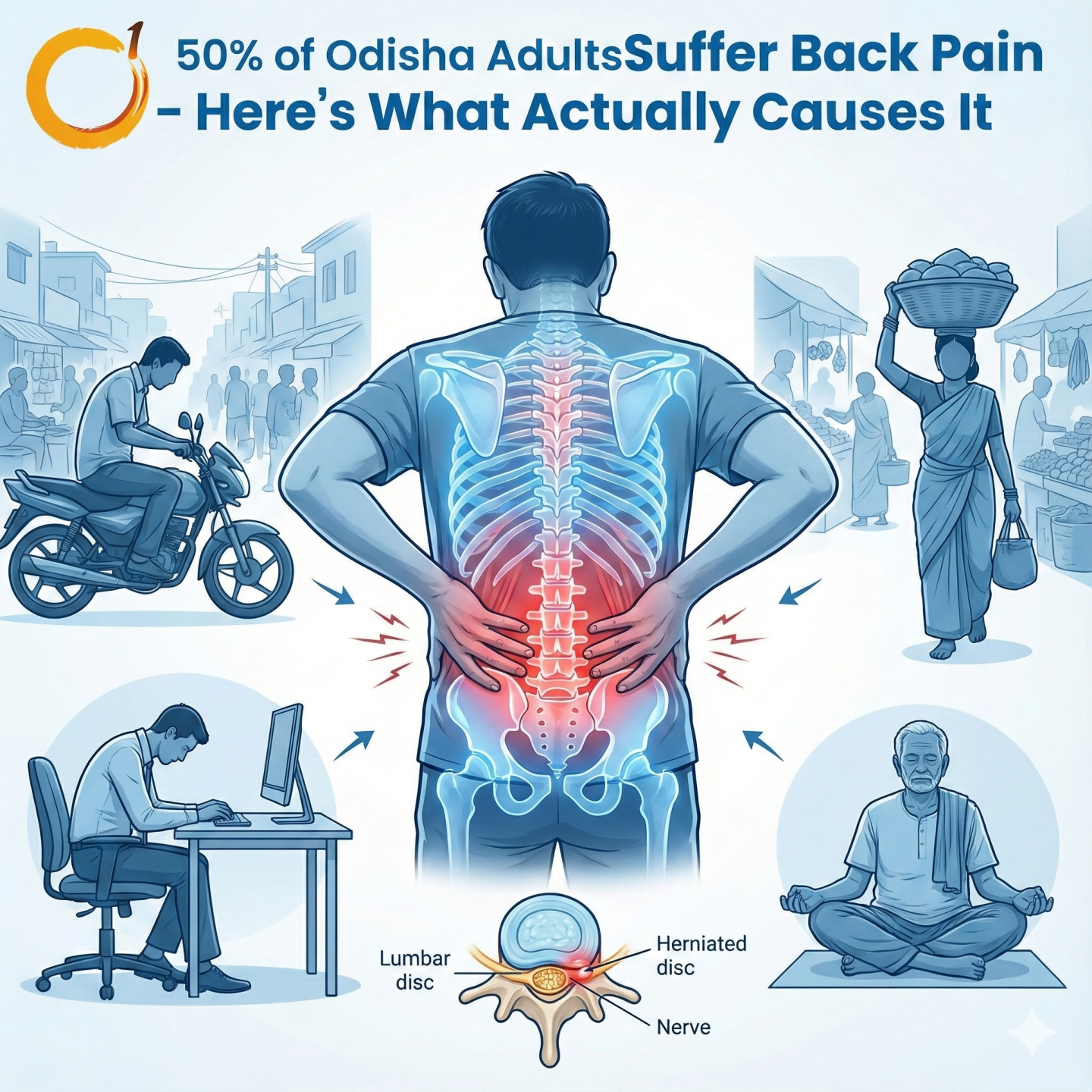
Limb injuries due to trauma, accidents, or congenital deformities can drastically affect mobility and quality of life. Limb reconstruction surgery offers patients a chance to regain function, correct deformities, and improve overall mobility.
At Orthoone Orthopedics, Bhubaneswar, we follow modern, evidence-based approaches to limb reconstruction, guided by Dr. Dibya Singha, ensuring safe procedures and faster recovery.
What is Limb Reconstruction Surgery?
Limb reconstruction is a specialized orthopedic procedure that helps:
- Correct bone deformities
- Treat non-healing fractures
- Restore length, alignment, and function of limbs
- Manage congenital limb deformities
It often involves external fixators, internal implants, or gradual bone lengthening techniques to restore normal function.
Who Needs Limb Reconstruction?
Patients with the following conditions may require reconstruction:
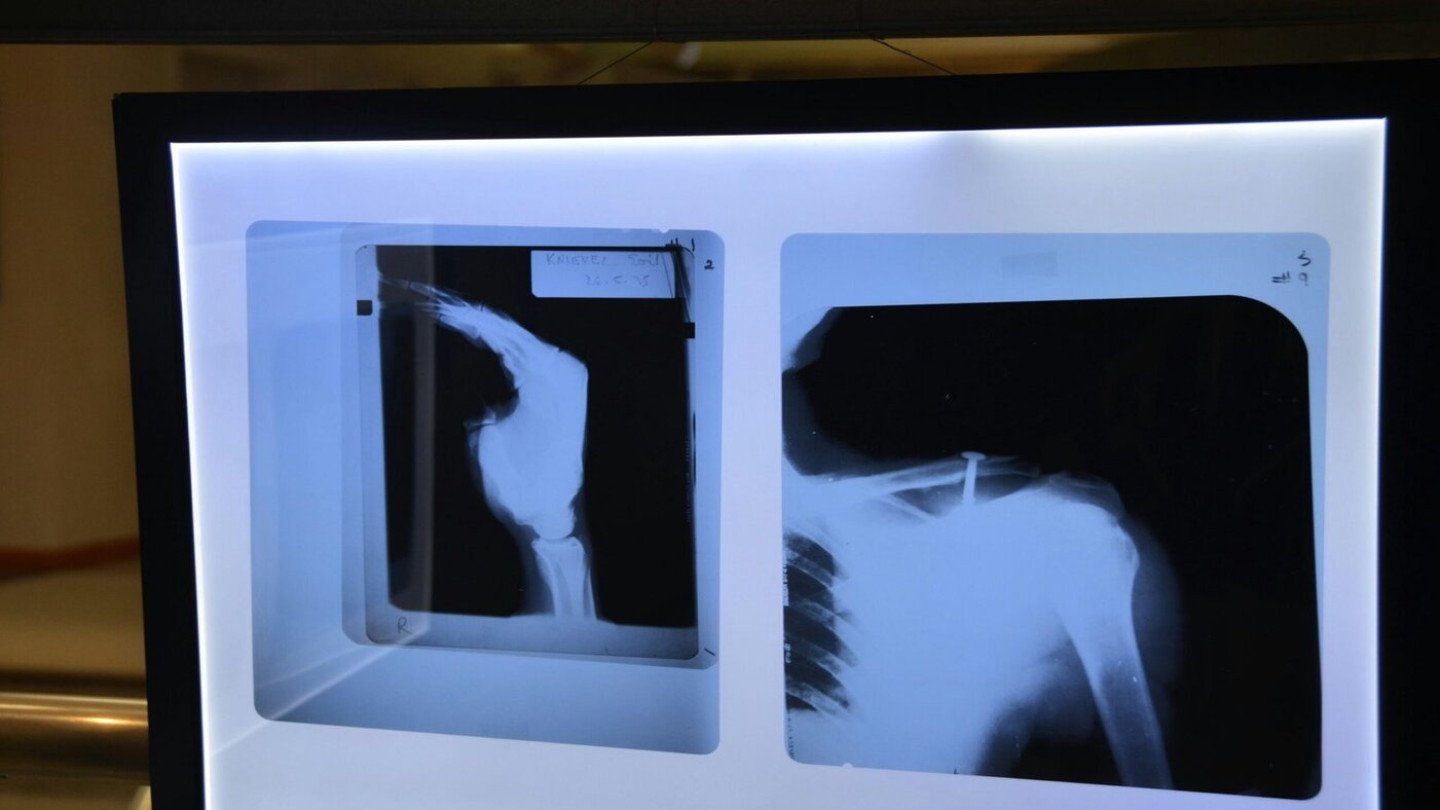
- Severe fractures or trauma that did not heal properly
- Bone infections (osteomyelitis) leading to deformity
- Congenital deformities in children or adults
- Limb length discrepancies
- Joint malalignment or severe arthritis
Early consultation ensures better planning and outcome.
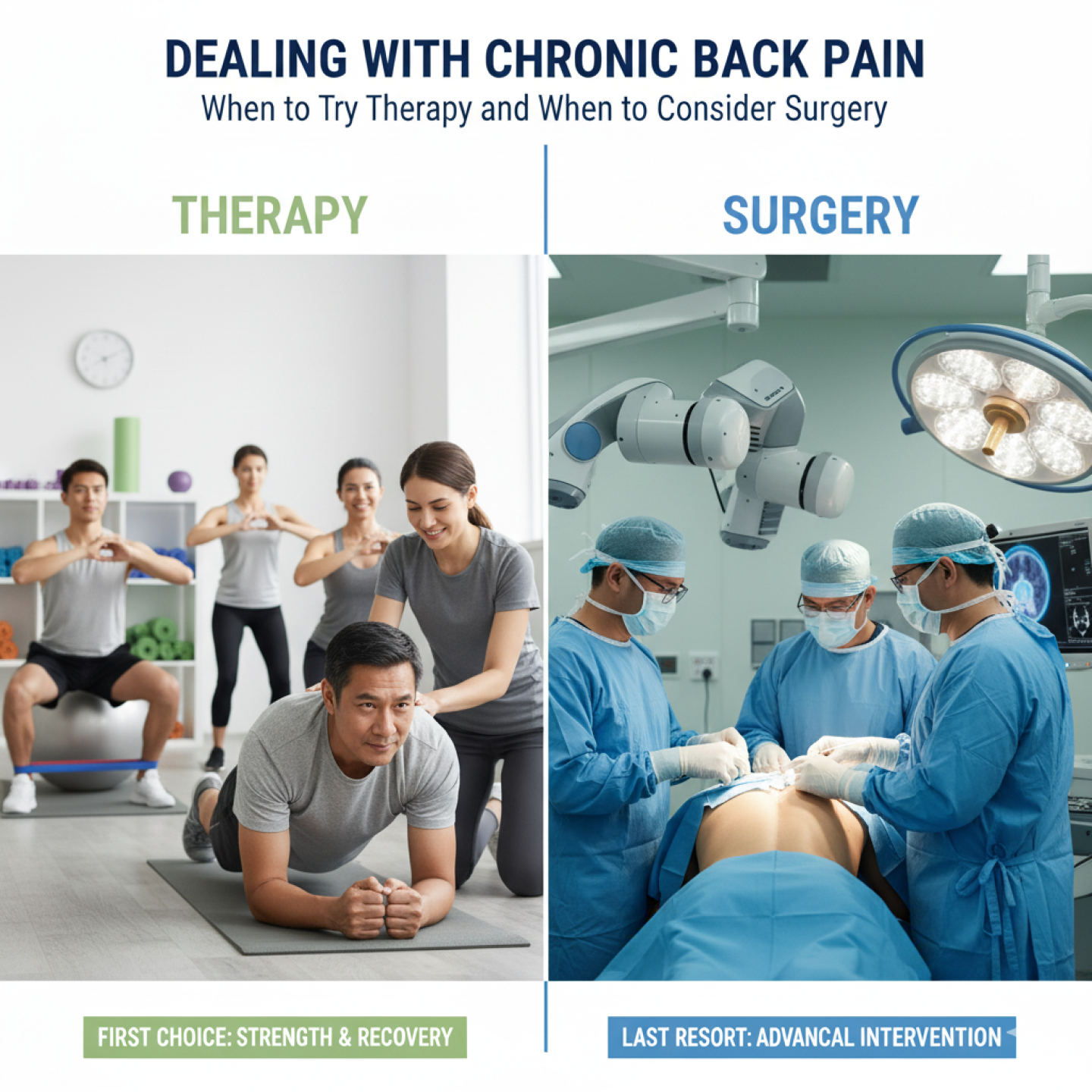
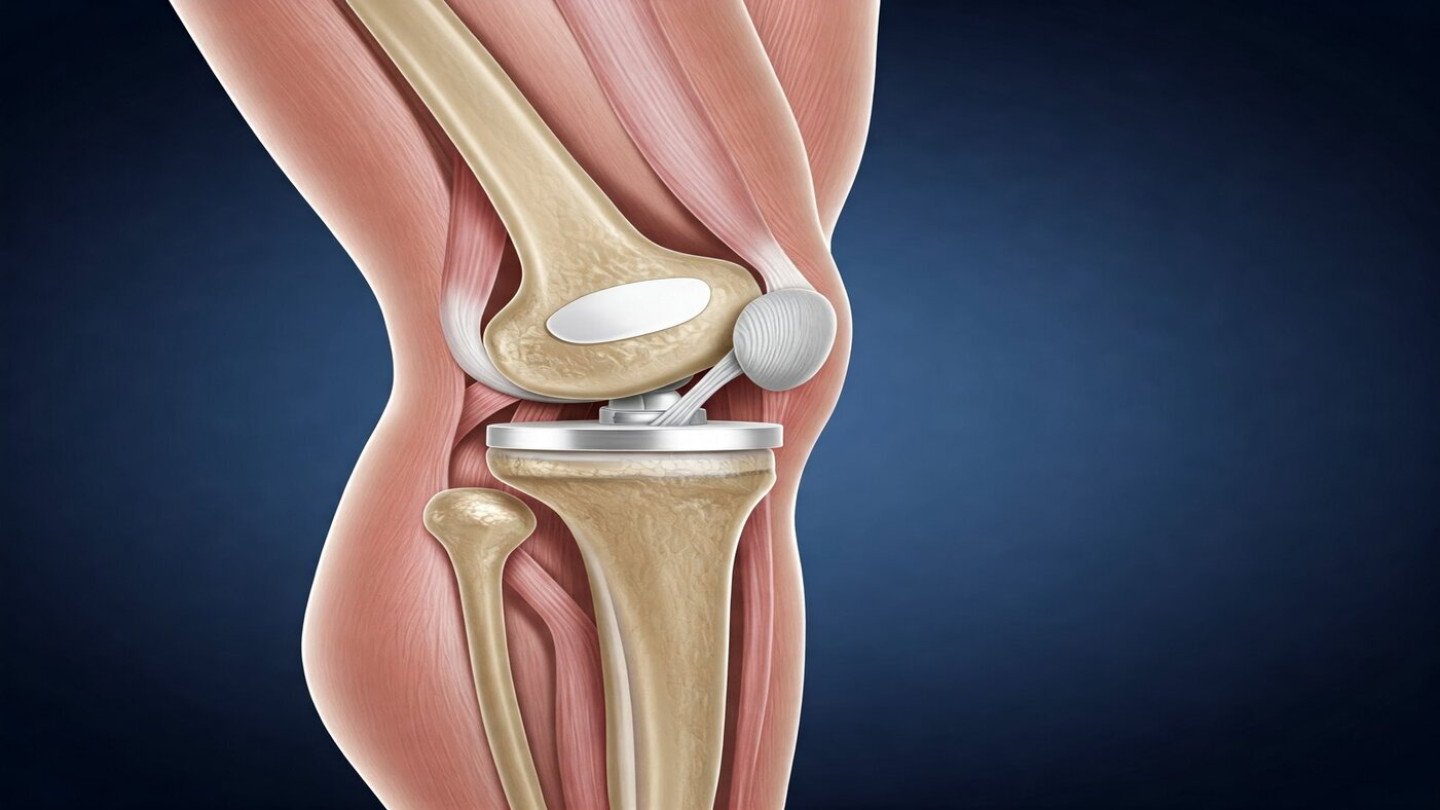
Modern Techniques in Limb Reconstruction
Orthoone Orthopedics uses state-of-the-art methods to ensure precision and safety:
- External Fixators – adjustable rods outside the body to align bones gradually.
- Internal Implants & Plates – internal support for stability and bone healing.
- Gradual Bone Lengthening – for limb length discrepancies using Ilizarov or other modern devices.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques – reduces tissue damage, infection risk, and recovery time.
These techniques are customized based on patient age, type of injury, and overall health.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Surgery is only part of the process. Structured rehabilitation is crucial:
- Physiotherapy to strengthen muscles
- Range-of-motion exercises
- Weight-bearing guidance
- Gradual return to daily activities and sports
With proper rehab, most patients regain excellent limb function within months.
Why Choose Orthoone Orthopedics?
Founded in 2015 by Dr. Dibya Singha, Orthoone Orthopedics has successfully treated thousands of patients with complex limb issues. Our approach combines:
- Expert orthopedic care
- Modern surgical techniques
- Personalized rehabilitation plans
- Focus on early recovery and functional restoration
Patients from Bhubaneswar, Odisha, and nearby states trust Orthoone for safe and effective limb reconstruction.
Take the First Step Towards Recovery
If you or your loved one suffers from trauma, deformity, or limb-length discrepancies, early evaluation is crucial.
Clinic Location:
Besides SBI ATM, Near Bus Stop, Acharya Vihar Square, Bhubaneswar
Call: 9439537777
Website: orthone.in
Regain mobility and confidence with modern limb reconstruction surgery at Orthoone Orthopedics.



Recent Comments